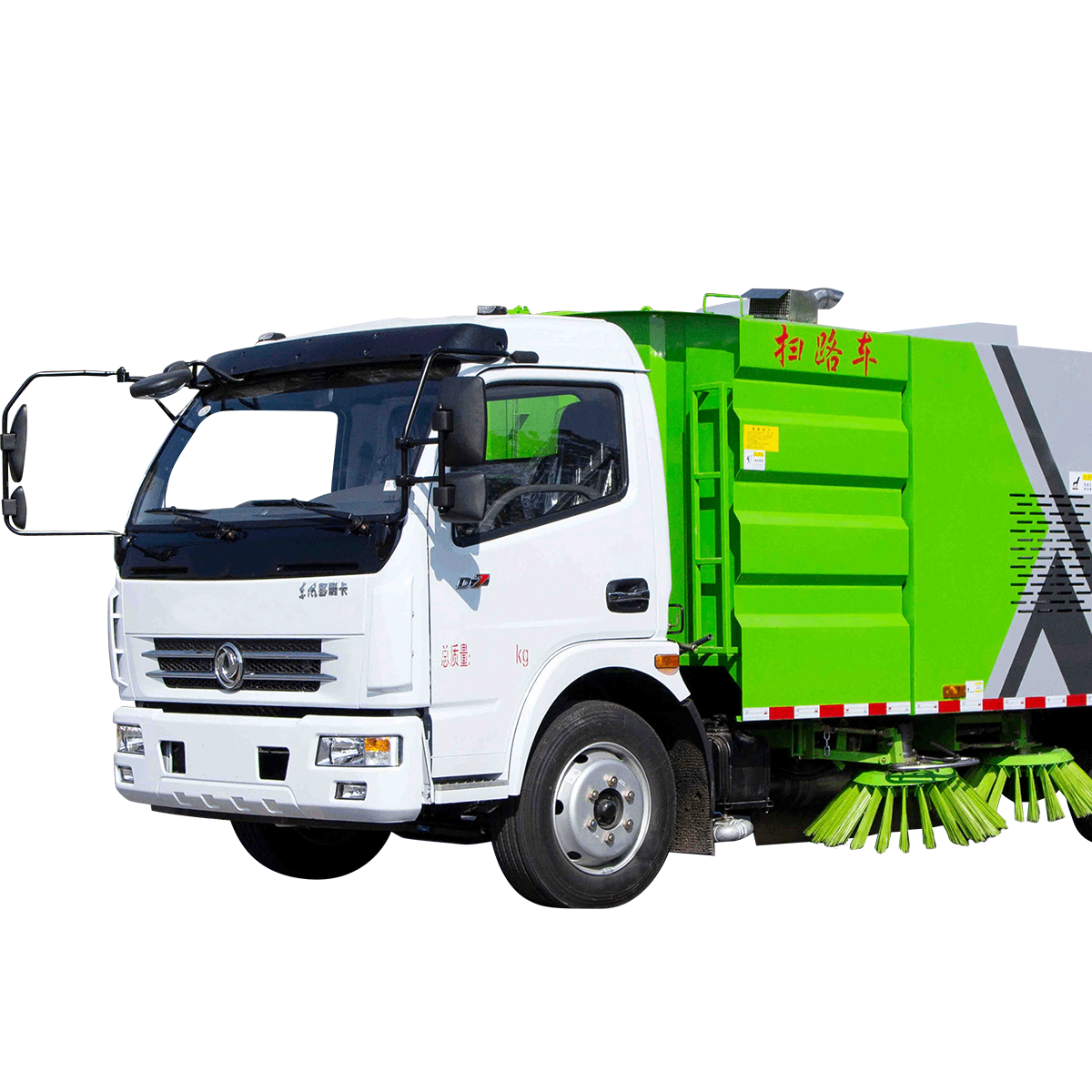
When purchasing an industrial floor scrubber/sweeper, it is important to consider the following key factors to ensure you select a device that meets your needs:
1. Cleaning Requirements
Cleaning Area Size: Choose a device with an appropriate sweeping width or scrubbing width based on the size of the area to be cleaned.
Floor Type: Consider the type of flooring, such as hard floors, carpets, or others, and select the appropriate brush or cleaning head.
Dirt Type: For different types of dirt, such as dust, liquids, oil stains, etc., select a device with adequate suction power, cleaning ability, and compatibility with chemical cleaners.
2. Functionality and Performance
Sweeping Width/Scrubbing Width: Determines the coverage area per cleaning pass, improving efficiency.
Suction Power/Cleaning Ability: Ensures the device can effectively remove all types of dirt.
Control Options: Choose between manual or automatic controls based on your needs.
Noise Level: Consider the noise level the device produces during operation to ensure it meets environmental requirements.
3. Power Type
Battery-Powered: Suitable for areas without power outlets, but consider battery life and replacement costs.
Corded: Continuous operation without worrying about battery life, but be mindful of cord length and safety.
4. Capacity and Storage
Debris Capacity: Large-capacity trash bins reduce the frequency of emptying, improving efficiency.
Water Tank Capacity: Ensure the fresh water and dirty water tanks have sufficient capacity to meet operational needs, avoiding frequent water refills or wastewater disposal.
5. Operation and Maintenance
Ease of Operation: Select a device with simple operation and an intuitive control panel.
Maintenance Requirements: Understand the device’s maintenance schedule, ease of replacing consumables, and the reliability of after-sales service.
6. Budget
Cost-Effectiveness: Select a device with high cost-effectiveness within your budget range, balancing price and performance.
Long-Term Operating Costs: Consider the device’s maintenance costs, replacement of consumables, and other long-term operating costs.